What is radio frequency identification technology (RFID)?
What is radio frequency identification technology (RFID)?
RFID radio frequency identification technology can be built into all areas of automatic data capture, and it mainly uses radio frequency (RF) to provide non-contact object identification. The current application fields of RFID radio frequency identification technology range from industrial automation, access control management, animal identification and electronic passports, to medical care, ticketing and inventory tracking. Today, RFID solutions have attracted much attention in the research and development plans of large enterprises. For example, the growth of the automatic identification field is indispensable to RFID radio frequency identification technology, which provides the basic technology required for contactless smart cards, production automation and electronic supply chains.
''The Near Field Communication (NFC) standard is based on short-range RFID high-frequency technology and supports 13.56 MHz. Today’s NFC products are all-encompassing. "
First, we will introduce the development history of RFID radio frequency identification technology, and then explain the application fields of RFID technology. Secondly, we discuss the technical aspects of data transmission and collection between different RF components in the RFID system. Finally, the RFID testing requirements during the development and installation stages will be introduced, as well as the RFID test equipment that can be used to execute and verify the test protocol. The advantages of using the demodulation capabilities of the latest generation auto-tuning spectrum analyzers and the latest versions of vector signal analysis software will also be highlighted.

RFID Technology Overview
RFID, also known as contactless IC cards or ID tags, is capable of detecting and identifying specific targets without direct contact with the target.
Different forms of RFID radio frequency identification technology have been developed for decades, and some basic forms were developed and used as early as World War II, such as Identification, Friend or Foe - IFF.

Since then, RFID technology development work has continued, and the basis of today's technology was mostly developed in the 1970s and 1980s. Widespread implementation of RFID radio frequency identification technology has become a challenge amid high costs and a general lack of standardization. As technology continues to evolve, it is possible to produce low-cost, disposable small "electronic tags", which has given the market a thriving scene, making the popularization of various RFID applications an achievable goal.
What is radio frequency identification RFID technology?
RFID is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency Identification, which is radio frequency identification. It is actually the specific application and development of automatic identification technology (AEI, Automatic Equipment Identification) in radio technology. The basic idea of this technology is to automatically identify target objects and obtain relevant data by using radio frequency signals. The identification work does not require manual intervention and can work in various harsh environments. RFID technology can identify high-speed moving objects and identify multiple tags at the same time, making the operation quick and convenient.
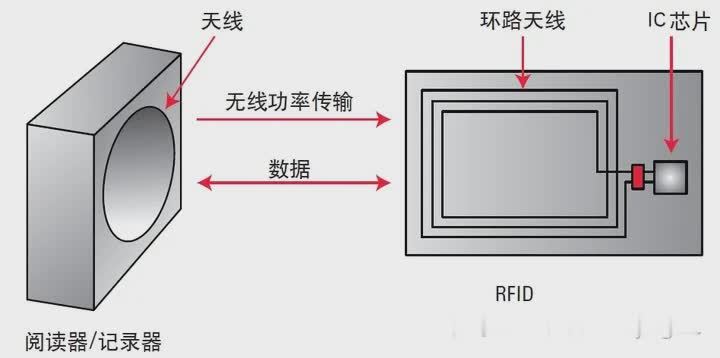
The figure shows a simplified RFID system model. The loop antenna in the reader/recorder communicates with the loop antenna in the RFID tag through electromagnetic coupling; the reader/recorder outputs a radio frequency signal, and the RFID tag receives the signal through the loop antenna. The RFID tag detects the DC signal of the detector circuit integrated in the IC chip to obtain energy and drive the IC chip.
How to evaluate RFID tags
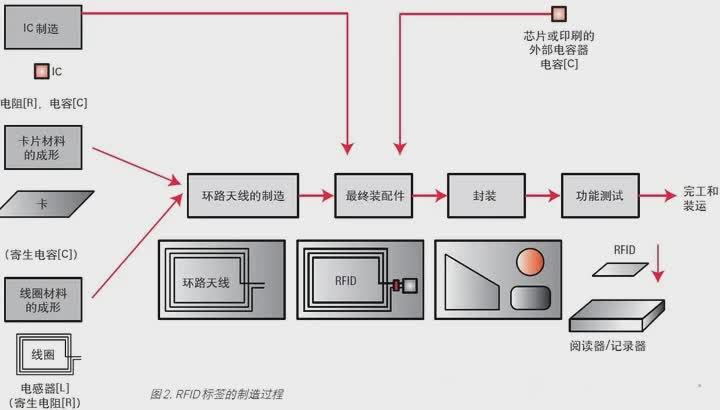
The figure shows a typical card-type RFID tag manufacturing process.
First, a loop antenna is formed on the card by printing or other means, and then the IC chip and chip capacitor are placed on the same card. Capacitors on the card can also be printed. Finally, the label is packaged, tested, and shipped.
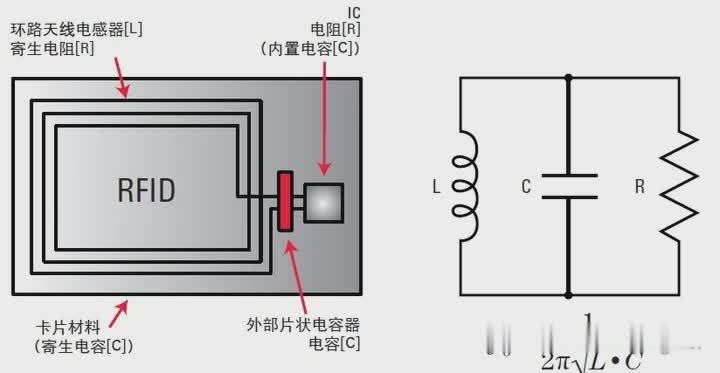
Generally speaking, RFID tags include an L-C-R parallel circuit (where "L" represents the loop antenna, "C" represents the chip capacitor, and "R" represents the IC chip). The resonant frequency f0 of the RFID tag can be calculated by the formula 1/(2π√LC). If the resonant frequency of the RFID tag is close to 13.56 MHz, it means that the RFID tag can maintain good communication with the reader/recorder. It is very important to verify that the resonant frequency of the entire tag is 13.56 MHz. At the same time, verifying the characteristics of L and C components can also help improve the overall RFID tag yield.
Another consideration is the sharpness of the resonance curve (communication bandwidth), which is determined by the R value of the IC chip or the parasitic resistance R value of the loop antenna.
When the bandwidth of the modulation signal is too wide, the sharpness of the resonance curve is too high, making communication difficult; on the other hand, the sharpness of the resonance is too low, which will cause the communication distance characteristics to deteriorate. Therefore, it is necessary to comprehensively measure the resonant characteristics of the complete tag and measure the resistance value step by step to help improve the communication performance of the RFID tag.

Navigation




