How are RFID tags used in smart railways?
What are the application scenarios, technical principles and future development prospects of RFID tags in smart railways?

With the rapid development of science and technology and the continuous increase of railway transportation volume, the traditional railway management model can no longer meet the development needs of modern railways. Therefore, it is an inevitable trend in the current railway development to realize the intelligence and efficiency of railway transportation with the help of Internet of Things technology. Among them, radio frequency identification technology (RFID), as a non-contact automatic identification technology, plays an important role in the construction of smart railways. This article will introduce the application background and significance of RFID tags in smart railways, as well as their specific application scenarios, technical principles and future development prospects in smart railways.
1. Application Background
The application background of RFID tags in smart railways mainly includes the following two aspects:
Advantages: RFID tags have the advantages of fast reading and writing speed, strong anti-interference ability, and batch processing. They can help the railway department improve the safety and reliability of transportation while achieving more efficient logistics management and ticket processing.
Disadvantages: Although RFID tags have many advantages, they are costly and may pose a risk of privacy leakage in some cases. Therefore, in practical applications, these factors need to be comprehensively considered to formulate a reasonable implementation plan.

2. Application Scenario
RFID tags have a wide range of application scenarios in smart railways, mainly including the following aspects:
(1) Automatic train station reporting: By installing RFID tags on trains and deploying readers at stations, the automatic train station reporting function can be realized. When the train approaches the station, the reader automatically reads the RFID tag on the train and sends the relevant information to the station staff, thereby realizing automatic station reporting.
(2) Passenger security inspection: Integrating RFID tags into passengers' identity documents or travel documents can quickly and accurately identify passengers during security inspections, improving the efficiency and accuracy of security inspections.
(3) Station equipment management: By pasting RFID tags on station equipment, real-time monitoring and precise management of station equipment can be achieved. For example, the energy consumption of air conditioning, lighting and other equipment in the station can be monitored and controlled in real time to achieve energy conservation and emission reduction.
3. Technical principles
The technical principles of RFID tags mainly include radio frequency technology and NFC technology.
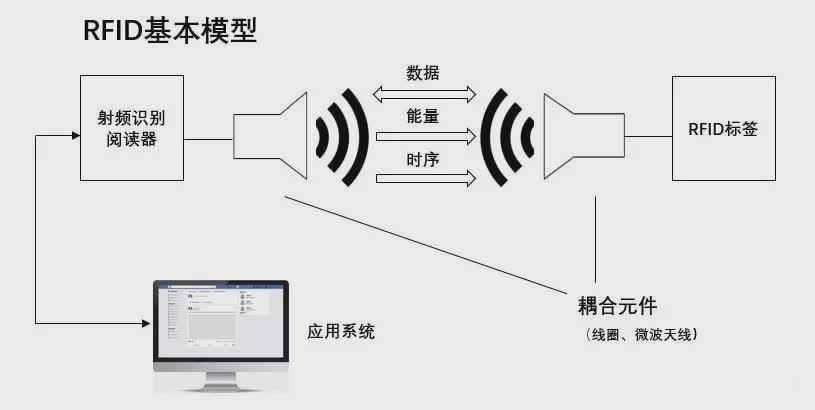
(1) Radio frequency technology: Radio frequency technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology that can realize the reading and writing operations of the reader through radio waves. In the RFID system, the reader/writer reads and writes the RFID tag by emitting electromagnetic waves. When an RFID tag enters the antenna coverage of the reader, it will receive the electromagnetic waves emitted by the reader and automatically send its own coded information. The reader can read and write the RFID tag by receiving the coded information.
(2) NFC technology: NFC technology is a short-distance communication technology that allows fast and secure communication between mobile devices. By using RFID tags with mobile devices, functions such as mobile payment and identity authentication can be realized. For example, in the railway ticketing system, passengers can use NFC-enabled mobile phones to authenticate and check tickets directly at the ticket gate without showing the ticket.
4. Practical Cases
(1) Economic benefits: The application of RFID tags in smart railways can help the railway department improve transportation efficiency and management levels, thereby reducing costs and improving benefits. For example, by implementing functions such as automatic station reporting and automatic ticket checking, labor costs and paper consumption can be reduced.
(2) Social benefits: The application of RFID tags in smart railways can improve the safety and reliability of railways. For example, by integrating RFID tags into passengers' identity documents, the accuracy and efficiency of security inspections can be improved and the occurrence of security incidents can be reduced. At the same time, the precise management function of RFID tags can also improve the service life and energy efficiency of station equipment, thus contributing to environmental protection.
5. Future Prospects
With the continuous development of technology and changes in market demand, the application prospects of RFID tags in smart railways are becoming increasingly broad. In the future, RFID tags may be combined with advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data to achieve more efficient and intelligent management and services. For example, by analyzing a large amount of data collected by RFID tags, valuable information can be extracted and applied to optimize transportation plans, improve logistics efficiency, etc. At the same time, with the development of wearable devices, RFID tags may be used in conjunction with smart bracelets, smart watches and other devices to provide passengers with more convenient and personalized services.
6. Conclusion
This article introduces the application background, application scenarios, technical principles, practical cases and future prospects of RFID tags in smart railways. By applying RFID tags to smart railways, many functions such as automatic train station reporting, passenger safety inspection, and station equipment management can be realized, thereby improving the transportation efficiency and management level of the railway, reducing costs and improving benefits. At the same time, the application of RFID tags can also improve the safety and reliability of railways and provide passengers with more convenient and personalized services. With the continuous development of technology and changes in market demand, the application prospects of RFID tags in smart railways are becoming increasingly broad.

Navigation




